Researchers Discover Zero-Day Vulnerability in 7-Zip Archiving Utility
Researchers said they recently discovered a zero-day vulnerability in the 7-Zip archiving utility that was actively exploited as part of Russia’s ongoing invasion of Ukraine.
The Vulnerability
The vulnerability allowed a Russian cybercrime group to override a Windows protection designed to limit the execution of files downloaded from the Internet. The defense is commonly known as MotW, short for Mark of the Web. It works by placing a “Zone.Identifier” tag on all files downloaded from the Internet or from a networked share. This tag, a type of NTFS Alternate Data Stream and in the form of a ZoneID=3, subjects the file to additional scrutiny from Windows Defender SmartScreen and restrictions on how or when it can be executed.
How the Vulnerability Worked
The 7-Zip vulnerability allowed the Russian cybercrime group to bypass those protections. Exploits worked by embedding an executable file within an archive and then embedding the archive into another archive. While the outer archive carried the MotW tag, the inner one did not. The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2025-0411, was fixed with the release of version 24.09 in late November.
Visual Representation
Tag attributes of outer archive showing the MotW.
Credit: Trend Micro
Inner Archive
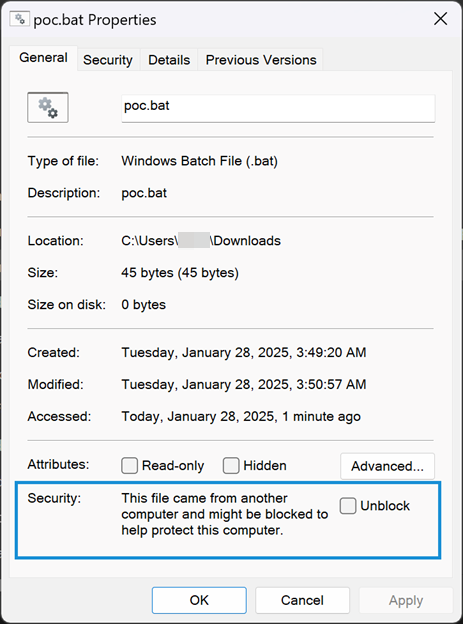
Attributes of inner-archive showing MotW tag is missing.
Credit: Trend Micro
Conclusion
The 7-Zip vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2025-0411, was a zero-day vulnerability that allowed a Russian cybercrime group to bypass Windows protections and execute malicious scripts or executables. The vulnerability was fixed with the release of version 24.09 in late November. It is essential for users to keep their software up-to-date to prevent such vulnerabilities from being exploited.
FAQs
Q: What is the Mark of the Web (MotW)?
A: The Mark of the Web (MotW) is a Windows protection that places a “Zone.Identifier” tag on all files downloaded from the Internet or from a networked share. This tag subjects the file to additional scrutiny from Windows Defender SmartScreen and restrictions on how or when it can be executed.
Q: How did the 7-Zip vulnerability work?
A: The 7-Zip vulnerability allowed the Russian cybercrime group to bypass MotW protections by embedding an executable file within an archive and then embedding the archive into another archive. While the outer archive carried the MotW tag, the inner one did not.
Q: Was the vulnerability fixed?
A: Yes, the vulnerability was fixed with the release of version 24.09 in late November.
Q: What should users do to prevent such vulnerabilities from being exploited?
A: Users should keep their software up-to-date to prevent such vulnerabilities from being exploited.

